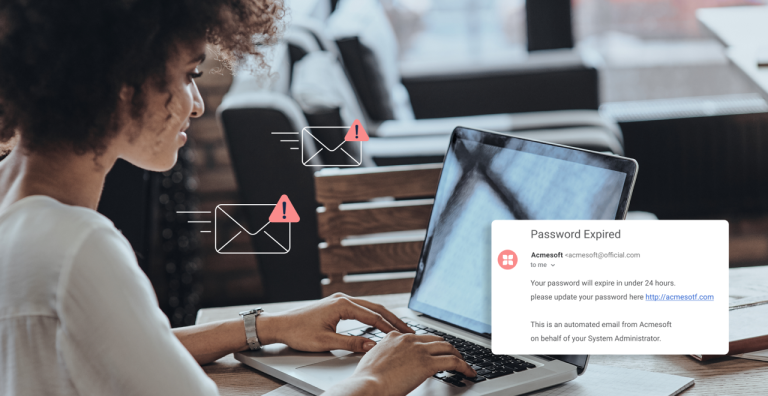
Phishing attacks are one of the most common and dangerous forms of cybercrime, designed to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or company credentials. These attacks often arrive through deceptive emails, fake websites, or malicious links, appearing to come from trusted sources like banks, clients, or even coworkers. By exploiting human trust and curiosity, cybercriminals can gain unauthorized access to personal or organizational data, leading to severe financial and reputational damage.
In recent years, the number of phishing incidents has skyrocketed globally, with businesses of all sizes facing targeted attacks daily. Remote work and increased digital communication have only amplified these risks. Since employees are the primary users of company communication channels, they become the first line of defense against phishing threats.
To build a strong security culture and reduce vulnerabilities, it’s crucial that every employee learns to recognize and respond effectively to phishing attempts. In this article, we’ll share 10 practical tips that help employees identify, avoid, and prevent phishing attacks — protecting both their personal data and their organization’s cybersecurity.
What Is a Phishing Attack?
A phishing attack is a fraudulent attempt by cybercriminals to obtain sensitive information such as login credentials, credit card details, or financial data by posing as a trustworthy entity. The goal is to deceive users into voluntarily sharing personal information or clicking on malicious links that compromise security.
Phishing comes in several forms. Email phishing is the most common, where fake emails mimic legitimate organizations. SMS phishing (smishing) uses text messages to lure users into clicking harmful links, while voice phishing (vishing) involves scammers making phone calls pretending to be from banks or IT departments. Spear phishing, on the other hand, is highly targeted and customized to deceive specific individuals or companies using personal details.
By exploiting trust and urgency, attackers trick users into revealing confidential data or downloading malware. Understanding these tactics is the first step toward recognizing and preventing phishing attempts effectively.
Why Employees Are Prime Targets
Cybercriminals often target employees because human error is easier to exploit than technical vulnerabilities. Even the most advanced security systems can be bypassed if an unsuspecting employee clicks a malicious link or downloads a harmful attachment. Attackers know that people tend to trust familiar names, act quickly under pressure, and overlook small details — making them the perfect entry point into a company’s network.
Through social engineering tactics, hackers manipulate emotions like fear, curiosity, or urgency to trick users into taking unsafe actions. For example, a fake email from a “manager” requesting an urgent payment or a “security alert” from a bank can easily fool an employee who isn’t cautious.
This is why awareness and education are crucial. Employees who understand how phishing works can spot red flags early, verify suspicious requests, and help protect the organization from costly breaches and data theft.
10 Tips for Employees to Prevent Phishing Attacks
1. Verify Email Senders Before Clicking Links
Always check the sender’s email address before responding or clicking on links. Phishing emails often appear legitimate but may include subtle changes in spelling or domain names. Confirm the sender’s authenticity by reviewing the email carefully and, if unsure, verify the request through a trusted communication channel. This habit can prevent exposure to malicious links and protect sensitive data.
2. Avoid Opening Suspicious Attachments
Attachments are a common method for delivering malware. Do not open files from unknown or unexpected sources, even if they appear to come from a coworker. Scan attachments with antivirus software and confirm with the sender if the file seems unusual. Avoiding suspicious attachments reduces the risk of malware infections and compromised systems.
3. Hover Over Links to Check URLs
Before clicking, hover over links in emails to view the actual destination URL. Phishing links may appear legitimate but redirect to malicious websites. Look for inconsistencies and verify that URLs match official company or service domains. This simple check can prevent credential theft and unauthorized access.
4. Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Enable multi-factor authentication wherever possible. MFA adds an extra verification step beyond passwords, such as a code from an authenticator app or a one-time SMS code. Even if a password is compromised, MFA prevents unauthorized access, significantly strengthening account security.
5. Keep Software and Email Filters Updated
Regularly update operating systems, browsers, antivirus programs, and email filters. Updates patch security vulnerabilities and improve phishing detection. Email filters can automatically identify suspicious messages, reducing the chances of accidentally interacting with phishing attempts.
6. Never Share Personal or Company Information via Email
Avoid sending sensitive information such as passwords, financial data, or identification details through email. Phishing attacks often request such data. Always confirm requests through official channels before sharing any information to prevent unauthorized access.
7. Be Cautious with Urgent or Threatening Messages
Phishing emails often create a sense of urgency or fear, pressuring employees to act quickly. Pause and evaluate any email that threatens account suspension, fines, or other urgent actions. Confirm the request through official communication channels before taking action.
8. Report Suspicious Emails Immediately
Notify your IT or security team immediately if you receive a suspicious email. Early reporting helps the organization block malicious senders, update filters, and prevent other employees from being targeted. Prompt action strengthens overall cybersecurity.
9. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
Create strong, unique passwords for each account using a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts. Strong passwords make it harder for attackers to gain access, even if one credential is compromised.
10. Attend Regular Cybersecurity Awareness Training
Participate in ongoing cybersecurity training programs. Awareness training and simulated phishing exercises help employees recognize evolving phishing tactics and reinforce best practices. Educated employees serve as a critical defense against cyber threats.
Conclusion
Phishing attacks remain one of the most significant threats to businesses today, exploiting human error and trust to gain access to sensitive information. Employees play a crucial role in defending against these attacks, as even the strongest technical safeguards can be bypassed if a user unknowingly interacts with a malicious email, link, or attachment.
By following the 10 practical tips outlined — including verifying email senders, avoiding suspicious attachments, hovering over links, enabling multi-factor authentication, keeping software updated, not sharing sensitive information, recognizing urgency tactics, reporting threats promptly, using strong passwords, and attending regular cybersecurity training — employees can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to phishing attempts.
Creating a culture of awareness and vigilance ensures that employees act as the first line of defense, helping protect both personal and organizational data. With consistent education and proactive habits, organizations can strengthen their cybersecurity posture, prevent costly breaches, and maintain trust among clients, partners, and stakeholders.